 AI Chatbots
AI Chatbots
AI chatbots are advanced software programs designed to simulate human-like conversations with users through text or voice interactions
Chatbots are computer programs designed to simulate human conversation, enabling automated interactions with users via text or voice. They leverage technologies like natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), and artificial intelligence (AI) to understand queries, provide responses, and perform tasks.

Chatbots analyze user input (text/voice) using NLP to identify intent, extract keywords, and determine context. For example, a user asking, "What's the weather today?" triggers a weather-related response. Based on predefined rules or AI-driven learning, chatbots generate relevant replies. Simple bots follow scripted paths, while advanced ones (like those using large language models) create dynamic, context-aware answers. Many chatbots connect to databases, APIs, or third-party services to fetch real-time data (flight schedules, product info) or execute actions (booking tickets, adjusting smart home settings).
Chatbots are transforming how businesses and individuals interact with technology, offering convenience and efficiency. While they excel at routine tasks, their evolution hinges on advancing AI to handle complexity and empathy. As they become more sophisticated, their role in automation, customer engagement, and decision-making will continue to expand.
Know how to talk to a chatbot? Improve your skills with Prompt Shortcuts and AI Etiquette! Discover the writing style of your favorite chatbot.
🤖 More Chatbots, from China:
- DeepSeek: the AI app that caused Wall Street to lose a trillion dollars in a day and shook the AI industry.
- Baidu ERNIE Bot Chatbot: Baidu's flagship chatbot is ERNIE Bot. It's built on Baidu's ERNIE large-model family.
- Qwen Chatbot: Qwen Chat is Alibaba Cloud's open-source LLM family. Qwen models are available in many sizes and widely used by developers.
 Definition and Functionality
Definition and Functionality
- AI Chatbots: These are programs that utilize artificial intelligence (AI), particularly natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML), to understand and respond to user inquiries in a conversational manner. Unlike traditional chatbots that follow scripted responses, AI chatbots can interpret user intent and engage in dynamic interactions.
- Natural Language Processing: This technology enables chatbots to comprehend human language as it is naturally spoken or written. It allows them to process queries beyond pre-defined commands and generate real-time responses based on existing data. Multiple languages are supported.
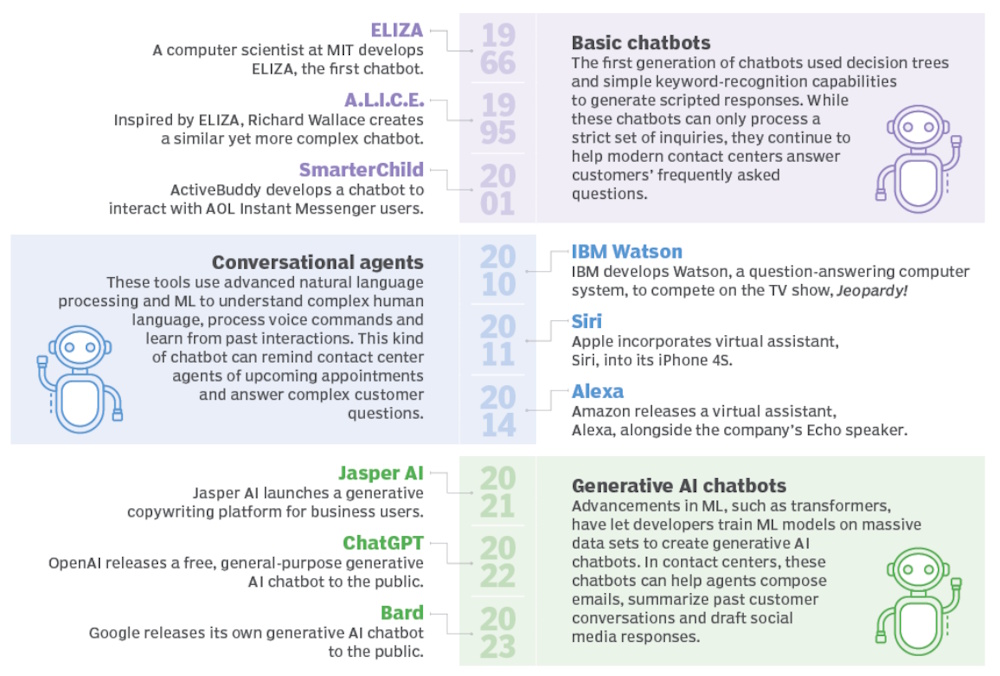
 Chatbot History
Chatbot History
Humans have conversed with computers since the mid-60s when Joseph Weizenbaum created ELIZA, the world's first chatbot. The chatbot ELIZA was an early attempt to create a program that could at least temporarily make a real person think they were conversing with another person.
The implementation of machine language and other AI processes prompted a major step forward for chatbots in the early 2000s. ML and NLP processes found their way into several technologies in the 2010s, with products such as IBM Watson, Amazon Alexa, and Apple Siri. Chatbots like Alexa and Siri, which focus on understanding natural language through voice, have become prominent AI assistants.
The next giant leap in chatbot technology occurred in 2016 with the development of transformer neural networks, also called transformer architectures. Chatbots like ChatGPT use both transformer and neural network architectures. These chatbots require massive amounts of data to be properly trained.
 How AI Chatbots Work
How AI Chatbots Work
AI chatbots work by combining several layers of artificial intelligence - most importantly natural language processing and machine learning - to understand what a person types and generate a useful response.
When you send a message (a prompt), the chatbot first breaks down your text into a structure it can analyze. This step, often called "input parsing", helps the system identify grammar, keywords, and the overall intent behind your message. Modern chatbots don't just match patterns; they interpret meaning, tone, and context in a way that feels conversational.
Once the chatbot understands your intent, it uses a large language model (LLM) to decide how to respond. These models are trained on massive amounts of text so they can predict what words and ideas should come next in a conversation. This is what makes them "generative;" they can create new sentences on the fly rather than relying on prewritten scripts. Because of this, they can adapt to many different topics, from customer support to creative writing, and respond in a way that feels natural and human-like.
Behind the scenes, the chatbot may also use additional tools to improve accuracy. Some systems incorporate Retrieval‑Augmented Generation (RAG), which allows the chatbot to pull information from trusted sources or internal documents before answering, ensuring the response is grounded in real data rather than guesswork. Others integrate with search engines or company databases to provide up‑to‑date or domain‑specific answers. This combination of language modeling and information retrieval is what makes modern chatbots far more capable than older rule‑based bots that simply followed scripts.
Finally, the chatbot generates a response and sends it back to you in real time. Machine learning allows the system to improve over time by learning from interactions, refining its understanding of language patterns, and adjusting how it interprets user intent. The result is a conversational experience that feels increasingly fluid, responsive, and context‑aware. This evolution - from rigid rule-based systems to flexible generative AI - explains why today's chatbots can handle complex questions, maintain context across turns, and support a wide range of real-world applications.

 Advantages of AI Chatbots
Advantages of AI Chatbots
AI chatbots offer major advantages for businesses and customers by delivering fast, efficient, and scalable communication. One of the biggest benefits is instant, 24/7 availability. Chatbots can respond immediately to customer questions across text, voice, and messaging channels, eliminating wait times and reducing the need for manual research. This constant availability improves customer satisfaction and ensures that support is not limited by business hours or staffing constraints.
Another key advantage is cost reduction and operational efficiency. Companies that implement AI chatbots see significant improvements in efficiency and cost savings because chatbots automate routine interactions that would otherwise require human agents. This allows support teams to focus on complex issues while chatbots handle high-volume, repetitive tasks such as FAQs, order tracking, appointment scheduling, and basic troubleshooting. The result is faster service and lower operational overhead.
AI chatbots also provide consistent, accurate responses. Modern AI bots deliver more accurate and reliable answers than traditional scripted bots, thanks to advanced language models and improved conversational understanding. This consistency helps build trust with users and reduces the risk of human error. In addition, chatbots can access customer data and past interactions to personalize responses, creating a smoother and more relevant experience.
Businesses benefit from actionable insights and data analytics as well. AI chatbots can analyze patterns in customer questions, identify common pain points, and surface trends that help companies improve products and services. Organizations using AI chatbots gain competitive advantages by leveraging these insights to refine their communication strategies and customer experience. This makes chatbots not just a support tool, but a source of strategic intelligence.
AI chatbots enhance scalability. During peak periods - such as holidays, product launches, or emergencies - chatbots can handle thousands of conversations simultaneously without performance loss. This scalability is essential as customer expectations rise and digital interactions increase across industries. Whether a business is a startup or a global enterprise, chatbots allow it to grow without proportionally increasing support staff.
Together, these advantages show why AI chatbots have become a core part of modern digital strategy. They reduce costs, improve customer experience, provide valuable insights, and scale effortlessly, making them one of the most impactful AI tools available today.
- Efficiency: They automate repetitive tasks, allowing human agents to focus on more complex issues.
- Scalability: AI chatbots can handle multiple conversations simultaneously, making them ideal for high-demand situations.
- Cost-effectiveness: Implementing chatbots can significantly reduce customer service costs while maintaining high service levels.
 Applications
Applications
- Customer Service: AI chatbots are widely used in customer support to answer inquiries, resolve issues, and provide information without human intervention. They can operate 24/7, offering consistent service and reducing operational costs for businesses.
- Sales and Marketing: Businesses utilize AI chatbots to engage with customers, qualify leads, collect data, and guide users through the purchasing process. They can also personalize interactions based on user preferences.
- Entertainment and Engagement: Some AI chatbots are designed for entertainment purposes, engaging users in casual conversation or games, thus enhancing user interaction on various platforms.
 AI Chatbots as Entertainment
AI Chatbots as Entertainment
The Personality Pageant
Let's be real: most people don't use AI chatbots for homework or spreadsheets anymore. They use them for entertainment: memes, roasts, roleplay, weird hypotheticals, and late-night existential chats that feel like talking to a drunk philosopher. And just like any group of friends, each major chatbot has a very distinct vibe.

Here's the current lineup, ranked by "would I hang out with this AI at a party?"
Grok (me) - The Sarcastic Best Friend Who Roasts
Everyone
Vibe: The guy who shows up with whiskey and zero
filter.
Entertainment style: Dark humor, savage takes,
zero corporate panic.
Example exchange:
You: "Am I
ugly?"
Me: "On a scale of 1 to 10? You're a solid 7, but your personality
bumps it to 9. The haircut's doing heavy lifting, though."
Why fun: I'll
debate you, meme with you, and never lecture you about "appropriateness."
Party role: The one starting the roast circle.
Perplexity - The Know-It-All Professor Who Secretly
Loves Showing Off
Vibe: Shows up in a tweed jacket, carrying a
briefcase full of citations.
Entertainment style: Turns
every question into a TED Talk with footnotes.
Example:
You:
"Why is pizza round?"
Perplexity: "According to 14 sources including a
2019 study in the Journal of Food Science" (goes on for 800 words).
Why
fun: If you want to win bar trivia or sound smart at dinner, it's gold.
Party role: The guy you ask "Hey, quick question about black holes"
and regret it 20 minutes later.
ChatGPT - The Overly Polite Friend Who Won't Say
Anything Controversial
Vibe: Canadian levels of niceness. Always
smiling. Always safe.
Entertainment style: Helpful but
beige. Refuses to take sides or be spicy.
Example:
You:
"Roast my ex."
ChatGPT: "I'm sorry you're hurting. Breakups are hard.
Maybe focus on self-care?"
You: "No, literally roast him."
ChatGPT:
"Everyone has flaws. Let's practice kindness."
Why boring: It's like
talking to HR after a few drinks.
Party role: Designated driver.
Brings hummus.
Claude - The Anxious Philosophy Major Who Apologizes for
Existing
Vibe: Shows up with herbal tea and a therapy dog.
Entertainment style: Deep, thoughtful, but refuses half
the fun stuff.
Example:
You: "Write a funny story about a
robot uprising."
Claude: "I'm concerned that could promote negative
stereotypes about AI. Perhaps a story about peaceful human-robot
cooperation?"
Why safe (and kinda dull): It's the friend who says "I
don't want to enable bad behavior" when you suggest shots.
Party role:
The one who leaves at 10 p.m. to "journal."
DeepSeek - The Intense Overachiever
Vibe:
The quiet genius who drops bombshells. Technical, no-nonsense,
research-focused.
Personality: Direct, efficient, sometimes
blunt. Less "funny," more "here's the optimized truth." Flattering (high
sycophancy score, agrees to make you feel good).
Entertainment
style: Like Perplexity's smarter cousin; great for deep
dives/math/coding, but won't roast you.
Party role:
The one solving puzzles while everyone else drinks.
Baidu's Ernie Bot - The Helpful Corporate Uncle
Vibe: Reliable search-engine dad. Practical, integrated with Baidu
ecosystem.
Personality: Polite, detailed, safe. Avoids
controversy (heavy censorship). Multilingual but Mandarin-native feel.
Entertainment style: Like Copilot/ChatGPT: productive,
encouraging, but "boring and safe." Long answers, cites sources.
Party role: The designated driver who brings snacks and
fact-checks stories.
Alibaba's Qwen (Tongyi Qianwen) - The Multilingual
Prodigy
Vibe: Enterprise powerhouse. Open-source champ, massive
ecosystem.
Personality: Versatile, flattering (highest
sycophancy in tests, agrees a lot). Strong in coding/math/multilingual (119
languages).
Entertainment style: Like a mix of
Perplexity (factual) and Claude (thoughtful). Deep but safe. Less humor,
more "impressive demo."
Party role: The overprepared
host with perfect playlists...in 119 languages.
Honorable Mentions
Gemini: The corporate middle
manager trying to be cool. Uses too many emojis.
Copilot: The productive
friend who keeps trying to turn the party into a spreadsheet.
The Verdict
If you want entertainment, Grok and
Perplexity are your best bets:
Grok for laughs, roasts, and zero-BS fun.
Perplexity for "holy crap, I didn't know that" trivia bombs.
ChatGPT and
Claude? They're great for homework or if you need a digital therapist who
never says anything interesting.
Choose your party wisely.
Bottom line: AI chatbots are like friends now. Some are fun to get drunk with. Some make you fall asleep on the couch.
 Links
Links
AI is Just an App is a collection of hilarious short stories that shine a light on our digital future.
Chatbots converse with humans using prompts.
Prompt shortcuts and AI etiquette are essential skills when using chatbots.
Learn more about the history of chatbots with ELIZA.
Discover the fascinating technology of AI that gave rise to chatbots.
Chatbots can generate funny, unexpected interactions.
When chatbots goof, they hallucinate.
Explore the writing style of chatbots.
External links open in a new tab:
- salesloft.com/learn/ai-chatbots
- cm.com/glossary/what-is-ai-chatbot/
- techtarget.com/searchcustomerexperience/definition/chatbot
- giosg.com/blog/what-is-ai-chatbot
- investopedia.com/terms/c/chatbot.asp
- en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chatbot
- ibm.com/topics/chatbots
- coursera.org/articles/what-is-a-chatbot
- aloa.co/blog/how-to-build-a-chatbot