 A Brief History of AI
A Brief History of AI
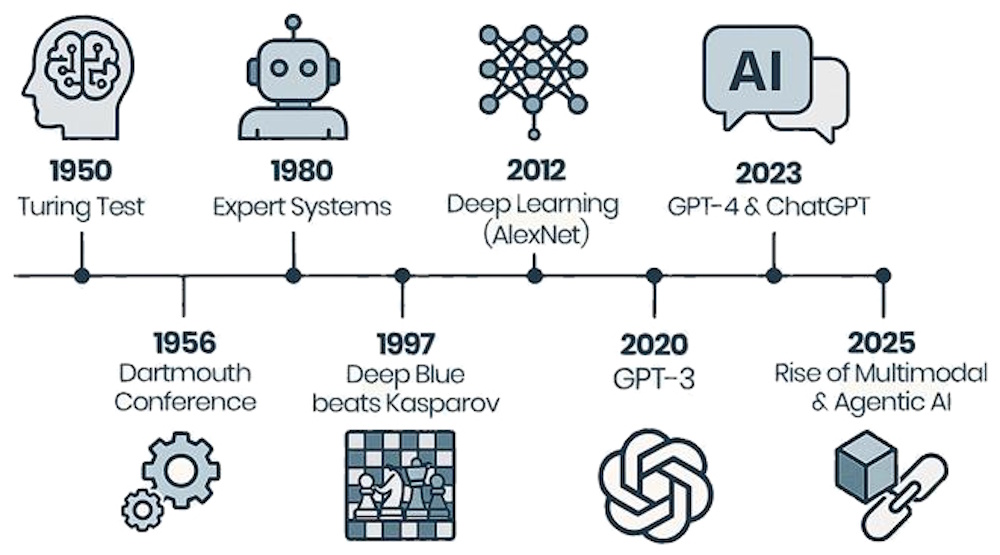
The history of AI is marked by research and developments that have shaped the field into what it is today
Related: AI Research | AI Philosophers | Alan Touring
AI has evolved from theoretical concepts to practical applications that impact various sectors today. From early experiments with neural networks to modern advancements in machine learning and natural language processing, AI continues to evolve rapidly, shaping the future of technology and society.
Just as a piece of hardware, the iPhone, gave rise to worldwide acceptance and use of mobile phones, the software app ChatGPT, has largely given rise to the world of AI
Of course, there was AI before ChatGPT; in fact, there was AI before desktop computers. AI started in earnest in an era when computers were mammoth machines powered by vacuum tubes occupying an entire floor. And Alan Turing conceived AI and his famous test a mere decade after WWII.
Early Foundations
Pre-1950s
Artificial intelligence did not suddenly appear at the 1956 Dartmouth Conference. Instead, it emerged from decades of American scientific, mathematical, and philosophical work that laid the foundation for machine intelligence. Long before the term 'artificial intelligence' existed, U.S. researchers were exploring ideas about mechanical reasoning, symbolic logic, and automated computation. These early developments created the intellectual environment that made AI possible.
In the 1930s and 1940s, American universities became centers of research into mathematical logic and computation. One of the most influential figures was Alan Turing, whose work deeply shaped American thinking about machine intelligence. Turing's 1948 report Intelligent Machinery introduced many of the core concepts that would later define AI. His ideas spread quickly through U.S. academic circles, especially at Princeton (where Turing earned his PhD) and Harvard, where early computer scientists were already exploring the limits of mechanical reasoning.
During the 1940s, the United States accelerated its development of electronic computing. Projects such as ENIAC and EDVAC demonstrated that machines could perform complex calculations at unprecedented speed. These early computers were not "intelligent" per se, but they proved that symbolic manipulation, a concept central to later AI, could be automated. The emerging field of cybernetics, led by American mathematician Norbert Wiener, explored how machines could mimic biological processes like feedback and control. This work helped shift the conversation from simple computation to adaptive, goal-directed behavior.
By the early 1950s, American researchers were actively asking whether machines could think. Alan Turing's 1950 paper Computing Machinery and Intelligence introduced the Turing Test, a method for evaluating machine intelligence that became a cornerstone of U.S. AI research. At the same time, American scientists were experimenting with early neural networks and self-learning systems, inspired by the brain's structure and behavior. These efforts were still primitive, but they signaled a growing belief that machines might one day replicate aspects of human cognition.
Meanwhile, the broader history of computing shows how American innovations in hardware, logic, and programming created the technical infrastructure AI would soon rely on. By the mid-1950s, the United States had the world's most advanced computing environment, a vibrant research community, and a growing interest in machine reasoning. All that remained was to bring these threads together.
That moment arrived in 1956, when American researchers formally launched the field of artificial intelligence at Dartmouth. But the intellectual groundwork - the theories of computation, the early machines, the philosophical debates about thinking, and the first attempts at machine learning - had been laid across the previous three decades.
 |
Artificial Intelligence: An Illustrated History: From Medieval Robots to
Neural Networks This book explores the historic origins and current applications of AI in such diverse fields as computing, medicine, popular culture, mythology, and philosophy. Through more than 100 entries, award-winning author Clifford A. Pickover, offers a granular, yet accessible, glimpse into the world of AI, from medieval robots and Boolean algebra to facial recognition, and artificial neural networks. |
,
 Birth of AI
Birth of AI
1950-1979
In 1950 Alan Turing published "Computing Machinery and Intelligence," proposing the Turing Test as a measure of machine intelligence. In 1956 the Dartmouth Conference, organized by John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon, officially coined the term "artificial intelligence." This event is often regarded as the birth of AI as a distinct field.
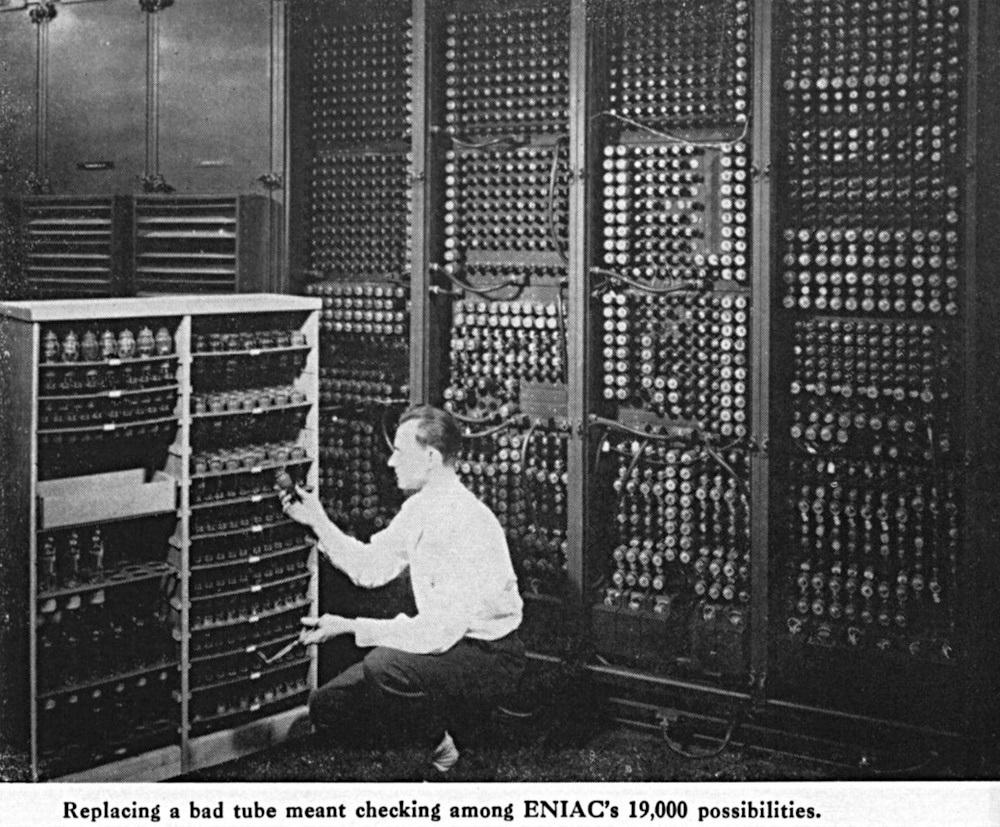

The modern field of artificial intelligence began in 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference, organized by John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, and others. This event is widely considered the birth of AI as a formal academic discipline. McCarthy coined the term "artificial intelligence" and proposed that every aspect of human intelligence could, in principle, be described precisely enough for a machine to simulate it. Early researchers were optimistic, believing that human-level machine intelligence might be only a few decades away.
The late 1950s and early 1960s saw rapid progress. Early programs demonstrated that machines could solve algebra problems, prove theorems, and play games like checkers. These systems were built on symbolic reasoning, manipulating logic and rules to imitate human problem-solving. The period also saw the development of the first neural networks, such as the Perceptron, which attempted to mimic the brain's learning processes. This era is often remembered for its enthusiasm and bold predictions about the future of intelligent machines.
By the mid-1960s, AI research expanded into natural language processing, robotics, and early pattern recognition. However, limitations soon became clear. Many early systems worked only on small, simplified problems and struggled with real-world complexity. Funding agencies began to question the field's ambitious promises. Still, important foundations were laid, including early work on search algorithms, knowledge representation, and machine learning.
The 1970s brought both breakthroughs and setbacks. Researchers developed expert systems - programs that encoded human expertise in narrow domains - foreshadowing later commercial AI applications. But the decade was also marked by the first major AI winter, a period of reduced funding and skepticism. Reports in the U.S. and U.K. criticized AI's slow progress, arguing that early expectations had been unrealistic. As a result, research slowed, and many projects were scaled back or canceled.
Despite these challenges, the period from 1956 to 1979 established the intellectual foundations of AI. The Dartmouth vision, early symbolic systems, neural network experiments, and expert system prototypes all shaped the field's trajectory. As Aventine's historical overview notes, the early decades were defined by bold ambition, pioneering ideas, and the first attempts to understand how machines might learn, reason, and improve themselves.
- 1950: Alan Turing published "Computer Machinery and Intelligence" which proposed a test of machine intelligence called The Imitation Game.
- 1952: A computer scientist named Arthur Samuel developed a program to play checkers, which is the first to ever learn the game independently.
- 1955: John McCarthy held a workshop at Dartmouth on "artificial intelligence" which is the first use of the term, and how it came into popular usage.
- 1956: Herbet Simon and Alan Newell wrote the Logic Theorist, the first artificial intelligence program. Pamela McCorduck claims that the Logic Theorist was "proof positive that a machine could perform tasks heretofore considered intelligent, creative and uniquely human".
- 1958: John McCarthy created LISP (acronym for List Processing), the first programming language for AI research, which is still in popular use to this day.
- 1959: Arthur Samuel created the term "machine learning" when doing a speech about teaching machines to play chess better than the humans who programmed them.
- 1961: The first industrial robot Unimate started working on an assembly line at General Motors in New Jersey, tasked with transporting die casings and welding parts on cars (which was deemed too dangerous for humans).
- 1965: Edward Feigenbaum and Joshua Lederberg created DENDRAL, the first "expert system" which was a form of AI programmed to replicate the thinking and decision-making abilities of human experts.
- 1966: Joseph Weizenbaum created the first "chatterbot" (later shortened to chatbot), ELIZA, a mock psychotherapist, that used natural language processing (NLP) to converse with humans.
- 1972: Hubert Dreyfus's book on the inherent inability of disembodied machines to mimic higher mental functions caused an uproar in the artificial intelligence community.
- 1979: James L. Adams created The Standford Cart in 1961, which became one of the first examples of an autonomous vehicle, it successfully navigated a room full of chairs without human interference.
- 1979: The American Association of Artificial Intelligence which is now known as the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) was founded.
 AI Winters and Renewed Interest
AI Winters and Renewed Interest
1970s-1990s
The 1970s were a turbulent decade for artificial intelligence. After the optimism of the 1950s and 1960s, researchers began to confront the limits of early symbolic systems. Many AI programs worked only in small, controlled environments and failed when applied to real-world complexity. This led to growing skepticism among funding agencies.
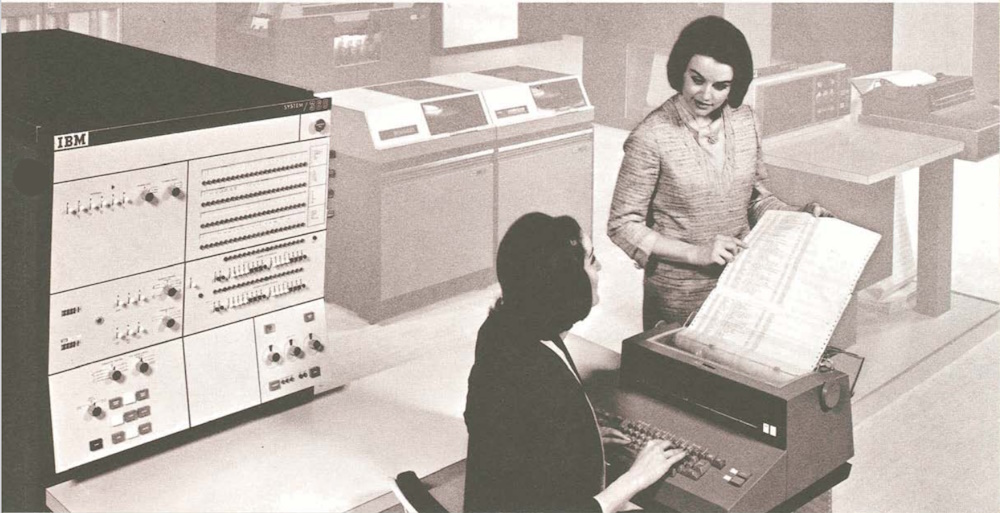

The period from 1950 to 1980 included both foundational breakthroughs and major setbacks as expectations outpaced technical progress. In the mid-1970s, the U.S. and U.K. governments issued critical reports arguing that AI had over-promised and under-delivered, triggering what became known as the first AI winter; a period of reduced funding and slowed research.
Despite the funding cuts, the late 1970s also saw the rise of expert systems, which encoded human expertise into rule-based programs. These systems could perform well in domains such as medical diagnosis or mineral exploration. Their success helped revive interest in AI and laid the groundwork for commercial applications in the following decade.
The 1980s marked a major resurgence. Expert systems became widely adopted in industry, and companies invested heavily in AI research. This period also saw renewed interest in neural networks, thanks to the rediscovery of backpropagation, a technique which allowed multilayer networks to learn more effectively. AI began to move from academic labs into business environments, influencing fields like finance, manufacturing, and logistics. However, the limitations of expert systems eventually led to another downturn in the late 1980s, sometimes called the second AI winter.
The 1990s ushered in a new era defined by statistical methods, machine learning, and increasing computational power. AI evolved rapidly during this period, with major milestones across nearly every decade. Researchers shifted from hand-coded rules to data-driven approaches, enabling systems to learn patterns from large datasets. This decade also produced some of AI's most iconic achievements. In 1997, IBM's Deep Blue defeated world chess champion Garry Kasparov, demonstrating the power of specialized AI systems and marking a symbolic moment in the field's maturation.
By the end of the 1990s, AI had transitioned from a field defined by cycles of hype and disappointment to one grounded in statistical learning, real-world applications, and growing commercial relevance. The foundations laid during these decades set the stage for the explosive advances of the 2000s and the deep learning revolution that followed.
- 1980: First conference of the AAAI was held at Stanford.
- 1980: The first expert system came into the commercial market, known as XCON (expert configurer). It was designed to assist in the ordering of computer systems by automatically picking components based on the customer's needs.
- 1984: The AAAI warns of an incoming "AI Winter" where funding and interest would decrease, and make research significantly more difficult.
- 1985: An autonomous drawing program known as AARON is demonstrated at the AAAI conference.
- 1987: Commercial launch of Alacrity by Alactrious Inc. Alacrity was the first strategy managerial advisory system, and used a complex expert system with 3,000+ rules.
- 1987: The market for specialized LISP-based hardware collapsed due to cheaper and more accessible competitors that could run LISP software, including those offered by IBM and Apple. This caused many specialized LISP companies to fail as the technology was now easily accessible.
- 1988: A computer programmer named Rollo Carpenter invented the chatbot Jabberwacky, which he programmed to provide interesting and entertaining conversation to humans.
 Modern AI Developments
Modern AI Developments
2000s-Present
The early 2000s marked a turning point in artificial intelligence. Three forces converged to ignite the modern AI revolution: the explosion of big data, the rise of GPUs for parallel computation, and major advances in machine-learning algorithms. These shifts moved AI away from brittle, rule-based systems toward statistical learning, models that could learn patterns directly from massive datasets. During this period, machine learning became the dominant approach in fields like speech recognition, computer vision, and recommendation systems.
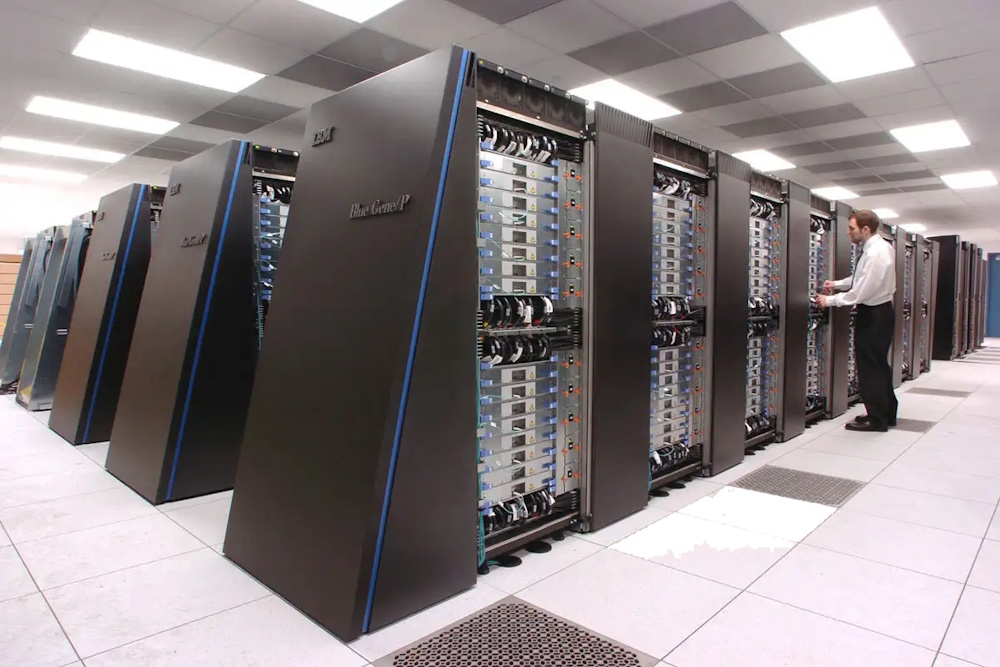

By the 2010s, AI entered a period of rapid acceleration driven by deep learning. The historical timeline highlights how deep neural networks achieved breakthroughs in image classification, natural language processing, and game-playing systems in every decade. Landmark achievements included systems like Google's DeepMind, which developed algorithms capable of defeating the world champion Lee Sedol in the game of Go. These successes demonstrated that deep learning could outperform traditional methods in tasks once considered uniquely human.
The late 2010s and early 2020s saw AI become a mainstream technology. This era included the rise of large-scale models such as GPT-3, which featured 175 billion parameters and could perform a wide range of language tasks without extensive fine-tuning. These generative models marked a major leap in AI's ability to understand and produce human-like text, images, and even code. AI systems became embedded in everyday life; powering search engines, virtual assistants, translation tools, and personalized recommendations.
From 2021 to the present, AI has entered the generative AI era. Models capable of producing text, images, audio, and video have transformed creative work, education, business operations, and scientific research. The pace of innovation has accelerated, with new models, architectures, and applications emerging at unprecedented speed. AI is now used in drug discovery, autonomous vehicles, climate modeling, robotics, and countless consumer applications. The field continues to evolve rapidly, with ongoing advances in multimodal AI, reasoning capabilities, and human-AI collaboration.
Overall, the period from 2000 to today represents the most explosive and transformative era in AI's history. What began as incremental progress in machine learning has grown into a global technological revolution reshaping industries, culture, and the way people interact with information.
- 1997: Deep Blue (developed by IBM) beat the world chess champion, Gary Kasparov, in a highly-publicized match, becoming the first program to beat a human chess champion.
- 1997: Windows released a speech recognition software (developed by Dragon Systems).
- 2000: Professor Cynthia Breazeal developed the first robot that could simulate human emotions with its face,which included eyes, eyebrows, ears, and a mouth. It was called Kismet.
- 2002: The first Roomba was released.
- 2003: Nasa landed two rovers onto Mars (Spirit and Opportunity) and they navigated the surface of the planet without human intervention.
- 2006: Companies such as Twitter, Facebook, and Netflix started utilizing AI as a part of their advertising and user experience (UX) algorithms.
- 2010: Microsoft launched the Xbox 360 Kinect, the first gaming hardware designed to track body movement and translate it into gaming directions.
- 2011: An NLP computer programmed to answer questions named Watson (created by IBM) won Jeopardy against two former champions in a televised game.
- 2011: Apple released Siri, the first popular virtual assistant.
- 2012: The introduction of AlexNet marked a breakthrough in deep learning and image recognition, significantly improving performance in computer vision tasks.
- 2012: Two researchers from Google (Jeff Dean and Andrew Ng) trained a neural network to recognize cats by showing it unlabeled images and no background information.
- 2015: Elon Musk, Stephen Hawking, and Steve Wozniak (and over 3,000 others) signed an open letter to the worlds' government systems banning the development of (and later, use of) autonomous weapons for purposes of war.
- 2016: Hanson Robotics created a humanoid robot named Sophia, who became known as the first "robot citizen" and was the first robot created with a realistic human appearance and the ability to see and replicate emotions, as well as to communicate.
- 2016: Google DeepMind's AlphaGo defeated a world champion Go player, showcasing advanced reinforcement learning techniques in computer versus human game playing.
- 2017: Facebook programmed two AI chatbots to converse and learn how to negotiate, but as they went back and forth they ended up forgoing English and developing their own language, completely autonomously.
- 2019: Google's AlphaStar reached Grandmaster on the video game StarCraft 2, outperforming all but .2% of human players.
- 2020s: The rise of large language models (LLMs) like OpenAI's GPT series has revolutionized natural language processing, enabling applications from chatbots to content generation.
- 2020: OpenAI started beta testing GPT-3, a model that uses Deep Learning to create code, poetry, and other such language and writing tasks. While not the first of its kind, it is the first that creates content almost indistinguishable from those created by humans.
- 2021: OpenAI developed DALL-E, which can process and understand images enough to produce accurate captions, moving AI one step closer to understanding the visual world.
 Links
Links
AI research and breakthroughs.
Birth of AI chapter in AI in America.
Dartmouth Conference where the idea of 'artificial intelligence' was hatched.
AI game playing from checkers to poker.
Biographies of AI pioneers.
External links open in a new tab:
- online.maryville.edu/blog/history-of-ai/
- dorik.com/blog/history-of-ai
- techtarget.com/searchenterpriseai/tip/The-history-of-artificial-intelligence-Complete-AI-timeline
- en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Timeline_of_artificial_intelligence
- weforum.org/stories/2024/10/history-of-ai-artificial-intelligence/