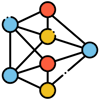
 Neural Networks
Neural Networks
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are a key technology in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) that mimic the way the human brain processes information
They consist of interconnected nodes, or "neurons," organized in layers, and are designed to recognize patterns, classify data, and make predictions based on input data. They represent a powerful approach to solving complex problems in AI by mimicking biological processes in the human brain. Their versatility and effectiveness have made them indispensable tools across various domains, driving advancements in technology and research. As AI continues to evolve, neural networks will likely play an even more significant role in shaping future innovations.

A neural network is a computational system inspired by the brain, built from interconnected layers of simple units that learn patterns from data. Their ability to generalize from examples makes them the foundation of today's most advanced AI systems.
A neural network is a type of machine-learning model designed to recognize patterns, make predictions, and learn from data by loosely imitating how the human brain works. A neural network is made up of many small processing units - called neurons or nodes - that are connected together in layers. Each neuron receives input, performs a simple mathematical operation, and passes the result to other neurons, allowing the network to build up complex understanding from simple parts. Neural networks can be thought of as groups of interconnected units that send signals to one another. The signals enable them to approximate complex functions and solve AI problems.
Neural networks learn by adjusting weights and biases, which determine how strongly each neuron influences the next. These models stack simple neurons in layers and learn pattern-recognizing parameters from data, mapping inputs (like images or text) to outputs (like labels or predictions). This learning process allows neural networks to improve over time without being explicitly programmed with rules.
Neural networks are powerful because they can identify patterns directly from data, enabling tasks such as image recognition, speech processing, and decision-making. They rely on components like activation functions, weighted connections, and learning rules to process information and refine their accuracy.
Neural networks are central to deep learning, a branch of machine learning where networks have many layers and can draw conclusions from unlabeled data with minimal human intervention. This is the technology behind modern breakthroughs in computer vision, natural language processing, and generative AI.
 Structure of Neural Networks
Structure of Neural Networks
Layers
- Input Layer: This layer receives the initial data for processing. Each node in this layer represents a feature or variable of the input data.
- Hidden Layers: These layers perform computations and transformations on the input data. A neural network can have one or more hidden layers, and each layer can have multiple neurons.
- Output Layer: The final layer produces the output of the network, such as classifications or predictions.
Neurons
Each neuron in a network processes inputs by applying a weighted sum followed by an activation function. The activation function determines whether the neuron should be activated based on its input.
Weights and Biases
Connections between neurons have associated weights that adjust during training, influencing the strength of the signal passed between neurons. Biases are additional parameters that help shift the activation function.
Learning Process
- Training: Neural networks learn from data through a process called training, where they adjust weights and biases based on the error of their predictions compared to actual outcomes. This is typically done using algorithms like backpropagation and optimization techniques such as gradient descent.
- Activation Functions: Common activation functions include sigmoid, ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit), and tanh, which introduce non-linearity into the model, enabling it to learn complex relationships.
 Applications of Neural Networks
Applications of Neural Networks
Neural networks are widely used across various fields due to their ability to handle complex data. Some notable applications include:
- Image Recognition: Used in facial recognition systems and medical imaging analysis.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Powers chatbots, language translation services, and sentiment analysis.
- Speech Recognition: Converts spoken language into text for applications like virtual assistants.
- Predictive Analytics: Used in finance for stock price prediction and risk assessment.
| What did the AI say after a long day of coding? |
 |
| "I'm exhausted, my neural network is fried!" |
 Types of Neural Networks
Types of Neural Networks
- Feedforward Neural Networks: The simplest type where connections between nodes do not form cycles; data moves in one direction from input to output.
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Specialized for processing grid-like topology data such as images; they use convolutional layers to automatically detect features.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Designed for sequential data processing; they maintain memory of previous inputs through loops in their architecture.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): Comprise two networks (generator and discriminator) that compete against each other to create new, synthetic instances of data.
 Links
Links
online.nyit.edu/blog/neural-networks-101-understanding-the-basics-of-key-ai-technology
elastic.co/what-is/neural-network
spiceworks.com/tech/artificial-intelligence/articles/what-is-a-neural-network/
techtarget.com/searchenterpriseai/definition/neural-network
ibm.com/topics/neural-networks
aws.amazon.com/what-is/neural-network/
cloudflare.com/learning/ai/what-is-neural-network/
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neural_net
sciencedirect.com/topics/earth-and-planetary-sciences/artificial-neural-network
nobelprize.org/prizes/physics/2024/press-release/