 Computer Vision
Computer Vision
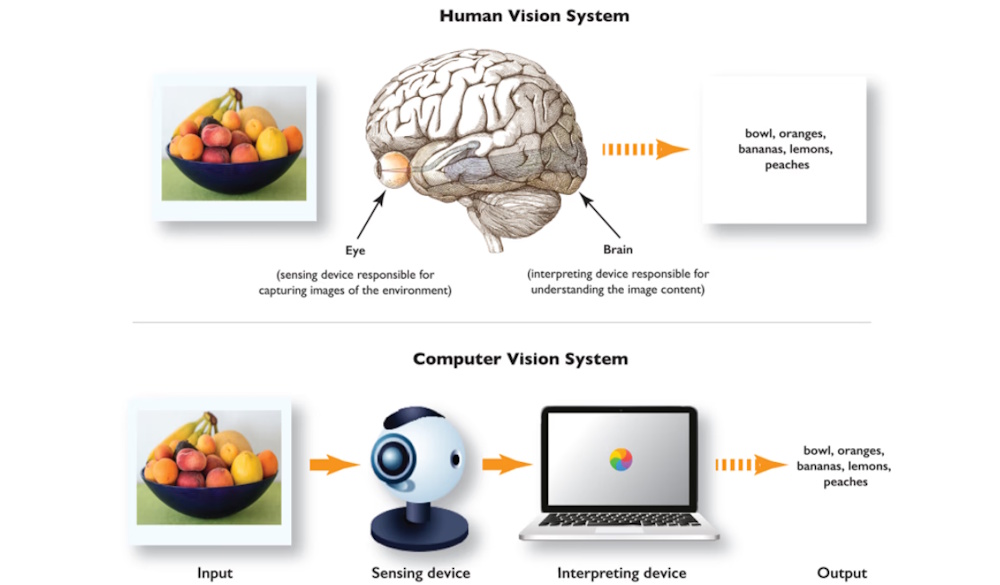
Like human vision, computer vision enables computers to interpret and understand visual information from the world around them
Computer vision is a major branch of artificial intelligence that enables machines to see, interpret, and understand visual information from the world. Computer vision is an AI subfield that allows systems to process, analyze, and interpret images and videos, extracting meaningful information from visual data. In other words, computer vision gives software the ability to "look" at the world and make sense of what it sees.

Computer vision systems use neural networks, machine learning, and deep learning algorithms to process images, similar to how humans put together a jigsaw puzzle. The network breaks down images into pixels, labels them, and then performs mathematical operations to make predictions. The network then iterates, checking the accuracy of its predictions until it starts to recognize images. As the technology continues to advance, computer vision is becoming increasingly integral to many AI-powered solutions, driving innovation in products and services.
Computer vision systems use machine language to automatically recognize images, classify objects, detect faces, and monitor environments, drawing from massive amounts of visual data captured by smartphones, cameras, and sensors. This makes computer vision essential for modern automation, safety, and analytics.
Computer vision involves methods for acquiring, processing, analyzing, and understanding digital images, transforming raw pixels into symbolic or numerical information that can guide decisions or actions. This includes tasks like recognizing objects, detecting motion, segmenting images, and interpreting scenes.
Computer vision helps machines understand visual information much like humans do, using techniques such as image processing, feature extraction, object detection, and image segmentation. These capabilities rely heavily on machine learning and deep learning, which allow systems to learn patterns from large datasets of labeled images.
Computer vision powers many real-world applications, including facial recognition, self-driving cars, medical imaging, robotics, and security systems. These systems use AI models to classify images, detect objects, track movement, and make decisions based on visual input.
 Computer Vision Use Cases
Computer Vision Use Cases
Computer vision is transforming industries by enabling machines to interpret and act on visual information. Computer vision delivers value by automating visual tasks, improving accuracy, and enabling new capabilities. From healthcare diagnostics to autonomous vehicles and retail automation, the technology is rapidly becoming a foundational part of modern AI systems. There are dozens of real-world applications of computer vision in industries like healthcare, retail, manufacturing, logistics, agriculture, security, and more. Below is an overview of some of the most important use cases.
🏥 Healthcare & Medical Imaging
Computer vision is widely used to analyze medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and retinal scans. Healthcare is one of the top sectors adopting computer vision, helping doctors detect diseases faster and more accurately. AI systems can detect diseases from retinal scans and interpret complex medical imagery in real time.
Examples: Tumor detection, Diabetic retinopathy screening, Surgical assistance, Radiology automation
🏭 Manufacturing & Quality Control
Manufacturers use computer vision to inspect products, detect defects, and monitor assembly lines. Vision systems can automate sorting, counting, defect detection, and safety monitoring across factories.
Examples: Detecting cracks, scratches, or misalignments, Monitoring worker safety, Automated assembly verification
🚗 Transportation & Autonomous Vehicles
Computer vision enables vehicles to understand their surroundings. Modern systems can navigate through fog, traffic, and complex environments using visual data.
Examples: Lane detection, Pedestrian and obstacle recognition, Traffic sign detection, Driver monitoring
🛒 Retail & E-Commerce
Retailers use computer vision to improve customer experience and optimize operations. There are applications in both online and in-store environments.
Examples: Automated checkout (e.g., Amazon Go), Shelf monitoring and planogram compliance, Customer behavior analytics, Inventory tracking
🚚 Logistics & Supply Chain
Computer vision helps track goods, automate warehouses, and improve accuracy in logistics. AIMultiple lists logistics as a major ROI-driven use case category.
Examples: Barcode and label reading, Package sorting, Damage detection, Fleet monitoring
🌾 Agriculture
Computer vision supports precision farming by analyzing crops, soil, and livestock.
Examples: Crop health monitoring, Weed detection, Yield estimation, Livestock tracking
🔐 Security & Surveillance
Computer vision powers modern security systems, enabling real-time monitoring and threat detection. Its notably used in large-scale public infrastructure monitoring.
Examples: Facial recognition, Intrusion detection, Crowd analytics, Fire and smoke detection
🤳 Consumer Technology
Computer vision is embedded in everyday devices. There are dozens of consumer-facing applications such as smartphones and smart homes.
Examples: Face unlock, AR filters, Gesture recognition, Home automation
🎮 Entertainment & Media
Computer vision enhances interactive experiences and content creation.
Examples: Motion capture, Sports analytics, Real-time video effects
🧪 Scientific & Industrial Research
Computer vision supports research in biology, chemistry, astronomy, and materials science.
Examples: Microscopy analysis, Satellite image interpretation, Environmental monitoring
 Components of Computer Vision
Components of Computer Vision
A complete computer vision system is built from several interconnected components that work together to capture, process, and interpret visual information. At the foundation is the input device, typically a camera or sensor, which captures raw visual data from the environment. This component functions like the human eye; collecting light and converting it into digital signals that the system can analyze. The quality of this input is crucial, since all later processing depends on the clarity, resolution, and accuracy of the captured images.
Once the visual data is collected, it is sent to the processing unit, which may include CPUs, GPUs, or specialized processors. This hardware performs the heavy computation required to analyze images, run algorithms, and extract meaningful information. The processing unit is responsible for executing the mathematical operations that power computer vision tasks, from filtering and feature extraction to object detection and classification. In many modern systems, GPUs are preferred because they can handle large volumes of parallel computations efficiently.
The next major component is the software layer, which includes the algorithms, libraries, and models that interpret the visual data. The core techniques of image processing, feature extraction, object detection, and segmentation form the backbone of computer vision software. These algorithms transform raw pixels into structured information, identifying edges, shapes, objects, and patterns that allow the system to understand what it is "seeing." This layer may also include machine learning or deep learning models trained on large datasets.
Finally, every computer vision system needs an output mechanism, which uses the results of the analysis. This is the component that converts processed data into outcomes. These are actions such as displaying results on a screen, triggering an alert, guiding a robot's movement, or feeding information into another software system. In many real-world applications, the output is not just visual but functional, enabling automation, decision-making, or real-time control.
Some sources also emphasize the importance of supporting hardware components. There are five key hardware elements (cameras, lighting, optics, frame grabbers, and processors) that ensure high-quality data capture and efficient processing in computer vision applications. These components help optimize image clarity, control environmental conditions, and manage data flow, especially in industrial or scientific settings.
Together, these components - input devices, processing units, software algorithms, output mechanisms, and supporting hardware - form the full pipeline of a computer vision system. Each part plays a critical role in enabling machines to interpret and act on visual information with accuracy and speed.
Key Concepts:
- Image recognition: Identifying objects, people, or scenes in images.
- Object detection: Locating specific objects within an image or video.
- Facial recognition: Identifying individuals based on facial features.
- Scene understanding: Interpreting the context and relationships between objects in an image.
Computer vision works through these steps:
- Image acquisition: Capturing visual data through cameras or sensors.
- Image processing: Enhancing and preparing the image for analysis.
- Feature extraction: Identifying key features or patterns in the image.
- Classification: Categorizing the identified features using machine learning models.
 Applications of Computer Vision
Applications of Computer Vision
AI computer vision applications are plentiful. Here are a few. See also the examples in the use cases above.
- Agriculture: Computer vision can monitor agricultural areas.
- Automotive: Enabling self-driving cars to navigate and detect obstacles.
- Document analysis: Computer vision can help extract visual elements from documents, such as images, signatures, logos, or stamps.
- Facial recognition: Computer vision can recognize faces in images and videos.
- Healthcare: Medical image analysis for diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Manufacturing: Quality control and defect detection on production lines.
- Medical imaging: Computer vision can help process medical imaging data, such as from CT scans and X-rays.
- Retail: Enhancing customer experiences through visual search and AR applications.
- Sports performance analysis: Computer vision can analyze sports performances.
 Links
Links
ibm.com/think/topics/computer-vision
uipath.com/product/ai-computer-vision-for-rpa
aws.amazon.com/what-is/computer-vision/
viso.ai/computer-vision/what-is-computer-vision/
arm.com/glossary/computer-vision