 AI Drones
AI Drones
are revolutionizing and, in some cases, alarming society with their advanced capabilities
Related: AI in our Everyday Lives
AI-powered drones are capable of operating with minimal human intervention, performing complex tasks that include navigation, data collection, and decision-making. AI drones are rapidly evolving, becoming more efficient, precise, and adaptable, and cheaper.
AI drones are classified as Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) that utilize AI to perform tasks autonomously and make smart decisions.
AI drones are used in many industries including defense, agriculture, disaster relief, security, and construction. They enhance efficiency, improve safety, and open up new possibilities for exploration and data collection. They are also subject to criticism since the use of drones in civilian spaces raises privacy concerns and legal issues.

 Key Features
Key Features
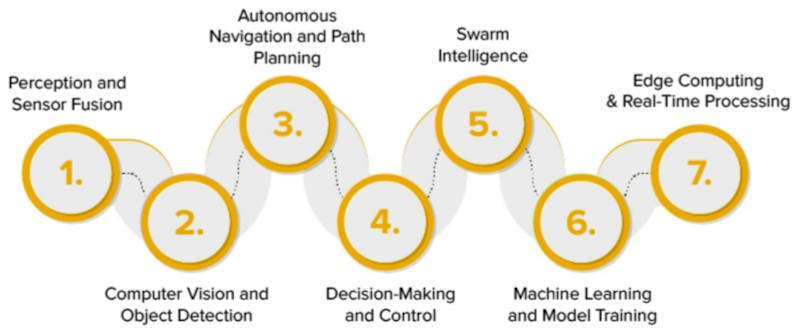
AI drones use machine learning, computer vision, and sensor mixing to handle data from sensors like cameras, LiDAR, thermal imaging, and others. The AI provides these features:
- Autonomous Navigation: AI enables drones to navigate complex environments and avoid obstacles. Using AI algorithms, drones can navigate without manual control, relying on GPS, cameras, and LiDAR. AI drones can navigate and fly without constant human input. They use advanced sensors, cameras, and software to perceive their environment and plan their flight paths.
- Computer Vision: Enables tasks like object recognition and real-time image processing.
- Intelligent Task Execution: These drones can perform specific tasks autonomously, such as monitoring crop health, conducting thermal imaging or delivering goods.
- Object Detection and Recognition: AI drones can identify and track objects, which is useful for applications like surveillance, search and rescue, and agriculture.
- Obstacle Avoidance: AI-powered sensors detect and avoid obstacles in real-time. Equipped with AI algorithms, these drones can detect and avoid obstacles in real-time, making them safer and more efficient.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI analyzes sensor data to forecast potential issues and reduce downtime.
- Real-Time Data Analysis: With edge computing, AI drones can process vast amounts of data in real-time, enabling quick decision-making and adaptive responses. Drones process vast amounts of data on-the-fly for quick decision-making. AI allows drones to process data onboard, reducing the need for remote computation.
- Swarm Coordination: AI coordinates multiple drones for complex missions and increased coverage. Drones can work collaboratively, mimicking behaviors observed in nature (e.g., flocks of birds or schools of fish).
 Hobbyist Drones from Amazon
Hobbyist Drones from Amazon
Bwine F7GB2 GPS Drones with Camera for Adults 4K, 3-Axis Gimbal, 2Mile Long Range, 75Mins Flight Time Professional Drone with 3 Battery, Auto Return+Follow Me+Fly Around+Beginner Mode for Kids
Ruko F11GIM2 Drones with Gimbal+EIS 4K Camera for Adults, 96 Min Long Flight Time 9800ft Long Range FPV, Auto Return Home with GPS, Foldable Quadcopter, FAA Remote ID Compliant
Potensic ATOM 3-Axis Gimbal 4K GPS Drone, Under 249g, 96 Mins Flight, Max 6KM Transmission, Visual Tracking, 4K/30FPS QuickShots, Lightweight for Adults and Beginners, Fly More Combo
X1 Self-Flying Camera, Pocket-Sized Drone HDR Video Capture, Palm Takeoff, Intelligent Flight Paths, Follow-Me Mode, Foldable Action Camera with Hands-Free Control

 Applications of AI Drones
Applications of AI Drones
The advanced capabilities of AI drones provide the potential to enhance operational efficiency, lower costs, and foster innovation in many industries, incliding:
- Agriculture: Practice precision farming by monitoring crop health, detecting pests, and optimizing irrigation. They are also used in pest and weed detection. Companies like DJI and XAG produce agricultural drones with AI capabilities. AI drones can increase crop production and promot eco-friendly farming.
- Construction: Monitoring construction progress and inspecting infrastructure such as bridges and pipelines. AI helps identify structural issues through pattern recognition.
- Delivery Services: Navigating urban landscapes for efficient package delivery. Companies like Amazon and Wing (Google) use AI drones for last-mile delivery. AI enables navigation, obstacle avoidance, and route optimization.
- Environmental Monitoring: Tracking wildlife, mapping ecosystems, and monitoring deforestation. AI drones collect and analyze large datasets in remote areas.
- Infrastructure: Inspecting bridges, pipelines, and power lines for defects. Improving safety and efficiency in infrastructure inspection.
- Logistics: Revolutionizing delivery services, especially in remote areas where other forms of delivery are time-consuming and costly.
- Military Operations: Enhancing target recognition, persistent surveillance, and adaptive mission planning. Surveillance and reconnaissance missions. Autonomous targeting and combat roles. The US military is transforming military strategy by using AI drones for battlefield situational awareness.
- Search and Rescue: AI drones are deployed in disaster zones to locate survivors using thermal imaging and advanced object detection algorithms. They are also used to support disaster management.
- Security and Surveillance: Detecting threats, monitoring borders, and identifying suspicious behavior.
 Types of AI Drones
Types of AI Drones
There are several types of drones, designed for specific uses. Each type of drone has its unique features and applications, making them suitable for different roles in different settings. Here are some common types:
-
Fixed-Wing Drones: These drones resemble traditional airplanes and are designed for long-distance flight and high-speed travel. They are often used for mapping, surveillance, and agricultural purposes.
-
Fixed-Wing Hybrid Drones (VTOL): Vertical Takeoff and Landing (VTOL) drones combine the features of fixed-wing and multi-rotor drones. They can take off and land vertically like a helicopter but fly like an airplane, making them versatile for various applications.
-
GPS Drones are equipped with GPS for precise navigation and waypoint tracking, often used in agriculture and surveying.
-
Large Combat Drones are high-altitude, long-endurance drones used for combat and strategic missions.
-
Micro Drones are small drones, often used for indoor navigation, hobbyist racing, and educational purposes.
-
Multi-Rotor Drones: These include quadcopters, hexacopters, and octocopters, which have multiple rotors (usually four or more). They are popular for their stability and ease of control, making them ideal for photography, videography, and hobbyist use.
-
Non-Combat Large Drones are used for tasks like cargo delivery, large-scale mapping, and environmental monitoring.
-
Photography Drones are designed for aerial photography and videography, popular among filmmakers, real estate agents, and hobbyists.
-
Racing Drones are built for speed and agility, used in drone racing competitions.
-
Reconnaissance Drones are designed for gathering intelligence and surveillance, often used in military and security operations.
-
Single-Rotor Drones: These drones have one main rotor and a tail rotor for stability, similar to a helicopter. They are efficient for longer flight times but can be more complex to control.
-
Small Drones are compact drones used for various recreational and commercial purposes.
-
Tactical Drones are used by military and law enforcement for reconnaissance, surveillance, and tactical operations.
-
Target and Decoy Drones are used in military training exercises to simulate enemy targets or decoys.
 Challenges and Concerns
Challenges and Concerns
- Data Security: The data gathered and generated by AI drones could be targeted by cyber attacks and misused if the data falls into the wrong hands.
- Regulation and Privacy: The use of drones in civilian spaces raises privacy concerns and legal issues. Regulatory bodies like the FAA in the U.S. govern drone operations.
- Security Risks: Potential misuse in surveillance, smuggling or malicious attacks. Drones can be vulnerable to hacking.
- Technical Limitations: Battery life and payload capacity are significant constraints for current AI drones.
 Future Prospects
Future Prospects
AI drones are expected to become more accessible with advancements in technology, such as better AI models, longer-lasting batteries, and less restrictive government regulations. Future applications include expanded use by the military, urban air mobility (air taxis), and fully autonomous drone fleets for commercial applications.
 Links
Links
wired.com/story/us-military-mystery-drones-response/ in the news
appinventiv.com/blog/ai-in-drones/
livescience.com/technology/robotics/defense-startup-developing-ai-kamikaze-drones-for-the-us-marines Bolt family of military drones
visionplatform.ai/artificial-intelligence-drones/
marketsandmarkets.com/blog/AD/ai-in-military-drones-game-changing-capabilities
reuters.com/technology/artificial-intelligence/ukraine-rushes-create-ai-enabled-war-drones
washingtonpost.com/technology/2024/12/04/openai-anduril-military-ai/
builtin.com/artificial-intelligence/drones-ai-companies
dronelife.com/ provides updates on drone technology
faa.gov outlines legal requirements in the USA and faa.gov/uas/getting_started/remote_id new rules for drones from the FAA