 GPTs
GPTs
GPTs, or Generative Pre-trained Transformers, are a family of advanced AI models designed to understand and generate human-like text. Where ChatGPT gets its name.
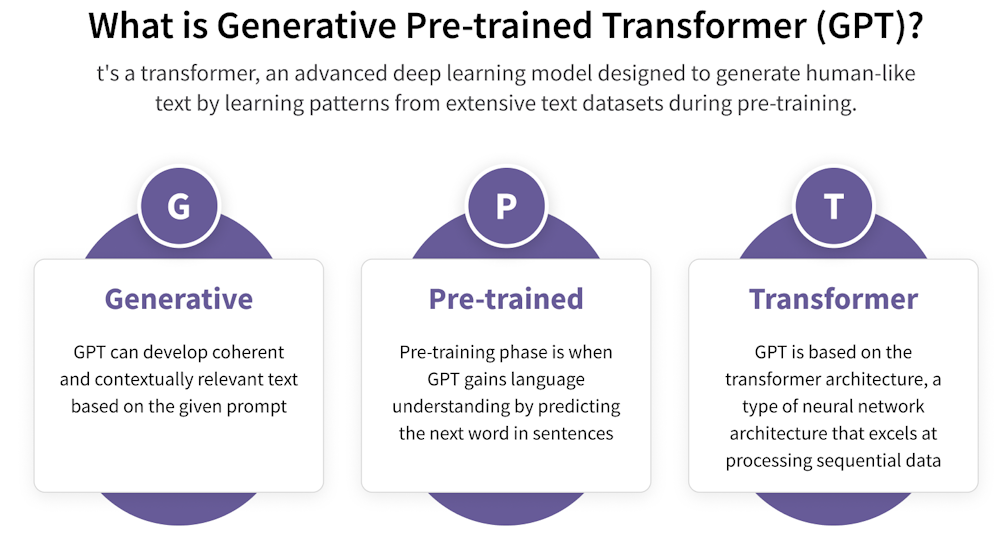
Generative Pre-trained Transformers, commonly known as GPTs, are a family of large language models built on the transformer deep-learning architecture. A GPT is a type of large language model widely used in generative AI chatbots, capable of producing novel content after being trained on massive datasets of unlabeled text.
These models are "generative" because they create new text, "pre-trained" because they learn from huge corpora before being fine-tuned, and "transformers" because they rely on the transformer architecture's self-attention mechanisms to understand relationships within language.
GPT models learn patterns, grammar, meaning, and relationships between words by analyzing enormous amounts of text during pre-training. GPTs use the transformer architecture introduced in 2017, which processes input in parallel using self-attention, allowing the model to handle long-range dependencies efficiently. After pre-training, the model can perform a wide range of language tasks - writing, summarizing, answering questions, translating, and even generating code - without needing task-specific training.
GPTs represent a major breakthrough in artificial intelligence. GPT models power applications like ChatGPT and other generative AI systems capable of simulating human-created output. Their ability to understand context, generate coherent text, and adapt to user prompts has made them foundational in modern AI. GPTs enable applications to produce human-like text and other content, supporting use cases such as chatbots, summarization, content generation, and search.
And GPTs can be customized versions of the base ChatGPT model, allowing users to tailor these AI tools for specific tasks or domains without requiring coding skills. This personalization enables the creation of specialized AI agents that can perform distinct roles in various settings.
 A Brief History
A Brief History
OpenAI introduced the first GPT model, GPT-1, in 2018, marking the first major application of generative pre-training to the transformer architecture. Since then, the GPT series has evolved rapidly, with models becoming larger, more capable, and increasingly multimodal. GPT versions 4 and beyond have expanded capabilities to include real-time processing of text, audio, and visual inputs.
The history of GPT models begins in 2018, when OpenAI introduced GPT-1, the first system to apply generative pre-training to the transformer architecture. GPT-1 marked the first major use of transformers for large-scale language modeling, trained on unlabeled text to generate coherent output. Though small by today's standards, GPT-1 demonstrated that a single model could learn general language patterns and perform multiple tasks without task-specific training.
In 2019, OpenAI released GPT-2, a dramatic leap forward. With far more parameters and a much larger training dataset, GPT-2 produced surprisingly fluent text, and consequently sparked global debate about the risks of releasing powerful generative models. GPT-2 was the moment when GPT models began to revolutionize the way machines understand and generate human language.
The breakthrough that pushed GPT into mainstream awareness came in 2020 with GPT-3. With 175 billion parameters, GPT-3 delivered unprecedented fluency, reasoning ability, and versatility. It powered early versions of ChatGPT and demonstrated that scaling up model size could unlock emergent capabilities. GPT-3 became the foundation for countless applications in writing, coding, tutoring, and creative work, and launched AI into public consciousness.
On 14 March 2023, OpenAI introduced GPT-4, a more capable and more aligned model that improved reasoning, safety, and multimodal understanding. GPT-4 could process images, handle complex instructions, and deliver more reliable outputs. GPT-4 marks the stage where GPT models began "pushing boundaries" and expanding beyond text into richer forms of intelligence.
The evolution continued with GPT-4o and GPT-5, which expanded real-time multimodal capabilities, processing text, images, audio, and more in a unified architecture.
The journey from GPT-1 to GPT-5 represents one of the fastest technological evolutions in history, with each generation bringing major advances in architecture, training scale, and real-world impact.
 Key Features
of GPTs
Key Features
of GPTs
GPTs are powerful because they combine generative ability, pre-training, and the transformer architecture into a single system capable of producing human-like text and multimodal content. Here are some of the key features of GPTs:
✨ General Intelligence & Reasoning
Modern GPTs (especially GPT-5 and GPT-5.2) show major improvements in complex reasoning, multi-step problem solving, logical consistency, and academic-level analysis. These models can follow long chains of thought and handle tasks that previously required human-level reasoning.
📝 Advanced Instruction Following
GPTs excel at understanding and executing detailed instructions. These include multi-part prompts, style-specific writing, structured outputs, and long-context tasks. This makes them highly adaptable for writing, coding, analysis, and workflow automation.
🧩 Multimodality
Newer GPTs can process and generate text, images, vision-based reasoning, and audio. This allows GPTs to understand charts, describe images, and integrate multiple forms of input.
💬 Natural, Context-Aware Conversation
GPTs maintain context over long interactions and produce responses that feel fluid and human-like. This means better memory handling, improved context retention, and more natural dialogue. This is why they work so well as assistants, tutors, and creative partners.
🛡️ Safety, Alignment & Controlled Output
Modern GPTs include safer responses, better refusal behavior, reduced hallucinations, and more accurate factual grounding. These improvements make GPTs more reliable for professional and educational use.
🧠 Pre-Training plus Fine-Tuning
GPTs are pre-trained on massive datasets, fine-tuned for instruction following, and aligned using human feedback. This combination gives them broad general knowledge and the ability to adapt to user intent.
💻 Code Generation & Technical Skills
GPT-5.2 shows major improvements in front-end UI code generation, spreadsheet understanding, and tool calling and API integration. GPTs can now build apps, write scripts, and automate workflows with minimal prompting.
📊 Token Efficiency & Long Context
Newer GPTs are more efficient. They use fewer tokens for the same task, handle longer documents, and maintain coherence across large contexts. This makes them better for research, legal analysis, and long-form writing.
🔧 Agentic Capabilities
GPT-5 and GPT-5.2 introduce early forms of agent-like behavior. This includes managing tools, executing multi-step tasks, and organizing context. This is a major step toward autonomous AI assistants.
 Applications
of GPTs
Applications
of GPTs
GPT models are now employed in consumer apps, enterprise tools, industry, etc. GPT-powered systems - especially ChatGPT - are used in work, creativity, productivity, customer service, and software development. Here are just a few examples of the many applications of GPTs:
🧠 Conversational Assistants & Chatbots
GPTs power natural, context-aware conversation in apps like ChatGPT. ChatGPT supports real-time voice conversations, photo-based queries, and general Q&A. These assistants help with everyday tasks, debates, language practice, and on-the-go problem solving.
✍️ Writing & Content Creation
GPTs are widely used for drafting emails, essays, and reports, creating marketing copy, and generating personalized greeting cards and creative ideas. ChatGPT explicitly supports creative inspiration and content generation.
🖼️ Image Generation & Visual Tasks
GPT-powered apps now include integrated image generation, built into the ChatGPT mobile app.
- Create original images from descriptions
- Transform existing images with text prompts
- Interpret photos and provide information about them
💼 Business Automation
There are dozens of business use cases where GPTs streamline workflows, including:
- Structured tasks
- Repetitive formatting
- Automated documentation
- Customer communication
GPTs help companies automate routine processes and improve efficiency.
🧪 Industry-Specific Integrations
GPTs are being integrated into products across many industries:
- E-commerce (product recommendations, chat support)
- Finance (report generation, customer queries)
- Healthcare (patient communication tools)
- Education (tutoring, content generation)
These integrations enhance digital products and services.
💻 Software Development
GPTs assist developers by generating code, explaining code, creating test cases, debugging, etc. Coding is one of the top GPT use cases.
🧭 Productivity & Personal Use
GPT-powered apps help users in many ways:
- Summarize documents
- Brainstorm ideas
- Plan schedules
- Learn new skills
The ChatGPT desktop and mobile apps support screenshots, files, and on-screen assistance.
🎨 Creative Workflows
GPTs support story generation, scriptwriting, brainstorming, music, art, etc. ChatGPT includes creative inspiration features for a wide variety of personal projects.
 Evolution of GPT Models
Evolution of GPT Models
The evolution of GPT models represents one of the fastest technological leaps in computing history.The journey began in 2018 with GPT-1, a 117-million-parameter model that demonstrated a surprising ability to complete sentences and perform basic language tasks. Though small by today's standards, GPT-1 proved that generative pre-training on large text corpora could produce a single model capable of many downstream tasks.
In 2019, OpenAI released GPT-2, a much larger model trained on a far broader dataset. GPT-2 generated coherent paragraphs, creative stories, and realistic text, sparking global debate about the risks of releasing powerful generative systems. Its success showed that scaling model size dramatically improved fluency and versatility.
The breakthrough moment came in 2020 with GPT-3, a 175-billion-parameter model that delivered unprecedented language fluency, reasoning ability, and general-purpose capability. GPT-3 powered early versions of ChatGPT and demonstrated that large-scale transformers could perform tasks like coding, tutoring, summarizing, translation, all without task-specific training.
By 2024, GPT-4 pushed the frontier further. GPT-4 is the "latest frontier" in the evolution of language models, offering stronger reasoning, better alignment, and early multimodal abilities such as image understanding. GPT-4 became the foundation for more reliable, safer, and more context-aware AI systems.
The evolution continued with GPT-5, which represents a "groundbreaking" step in the history of OpenAI models, expanding capabilities in planning, reasoning, and multimodal processing. GPT-5 and its successors introduced more agent-like behaviors, improved tool use, and more advanced real-time processing.
Some analyses even describe eight generations in seven years, emphasizing how quickly GPT models have advanced. Behind each release were major shifts in engineering, training scale, and policy experimentation that shaped the trajectory of modern AI.
 Key Products
Key Products
ChatGPT is an advanced AI chatbot developed by OpenAI that utilizes natural language processing (NLP) to generate human-like conversational dialogue.
DALL-E2 is an AI system that can create realistic images and art from a description in natural language. See also Nano Banana.
AutoGPT goes beyond traditional language generation tools by incorporating data from multiple sources, including news articles, and scientific data sources. This allows the system to generate text that is not only accurate but also reflects the latest trends and developments in your field.
AgentGPT allows you to create an agent by adding a name / goal, and hitting deploy. For example:
- ResearchGPT - Create a comprehensive report of the Nike company
- TravelGPT - Plan a detailed trip to Hawaii.
- StudyGPT - Create a study plan for a History 101 exam about world events in the 1980s
 Links
Links
writesonic.com/blog/what-are-gpts
servicenow.com/it/ai/what-is-gpt.html
coursera.org/articles/what-is-gpt