 AI Robotics
AI Robotics
Combining AI and robotics to create incredible machines
AI robotics is a multidisciplinary field that combines AI and robotics to create machines capable of autonomously performing tasks. The integration of AI into robotic capabilities has transformed industry leading to incredible advancements in efficiency and productivity. The development of intelligent robots has reshaped labor markets, driven innovation, and raised ethical questions. The ethical issues highlight the need to unpack the implications of these technologies on employment, privacy, safety, and more.
The history of AI robotics can be traced back to early automation concepts. Milestone events include Unimate, the first programmable robot deployed in industrial settings. This marked the beginning of a new era where robots began to automate labor-intensive tasks, evolving from simple machines to complex systems that apply machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing.
Robots have been developed for a number of applications, from virtual health assistants that enhance patient interaction, to collaborative robots or cobots that automate manufacturing plants, to autonomous vehicles that explore another planet. The integration of advanced sensor technologies and AI-enabled autonomous decision-making has allowed robots to quickly adapt to dynamic environments. The rapid development of these technologies in industry is accompanied by several challenges, including high implementation costs and concerns about job displacement.
The cultural impact of AI robotics has been significant, influenced by Hollywood movies and literary works such as Isaac Asimov's "Robot" series, which have sparked public interest in autonomous systems, especially whether robots are a threat to society. Instead of a threat, Elon Musk refers to his Optimus robot under development as a "buddy".
Looking to the future, the collaboration between humans and AI robotics holds great promise, potentially unlocking new capabilities and improving the quality of life. As these technologies continue to evolve, it is important to carefully consider their implications and develop a collective understanding of how best to integrate AI robotics into society.
 History
History
AI robotics can be traced back to the early days of automation and artificial intelligence
While the roots of robotics date back to ancient civilizations, it wasn't until the early 20th century that the field took shape. In 1954 George Devol invented Unimate, the first programmable robot. This groundbreaking innovation was designed for industrial automation applications. By the 1960s, it was deployed in General Motors' production lines, forever changing manufacturing with the automation of labor-intensive tasks.
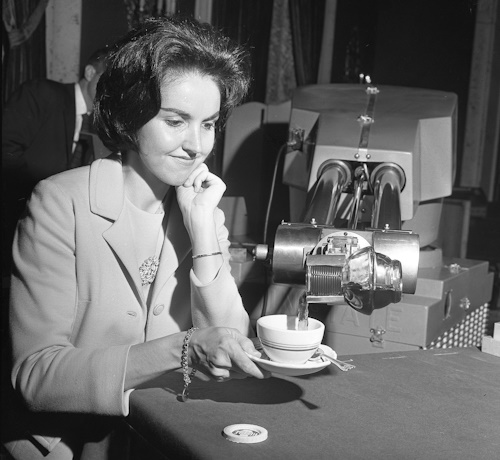

Unimate pouring coffee for a worker
As robotics developed, the integration of AI began to enhance robotic capabilities. Isaac Asimov's "Three Laws of Robotics" reflected a growing interest in autonomous systems. His Robot series in the 1960s revolutionized AI literature with the Three Laws. These laws, which governed the behavior of robots in Asimov's universe, became foundational in science fiction. They stipulated that robots must protect humans, obey orders, and preserve their existence, provided these actions don't conflict with the initial two laws. The Robot series sparked broader cultural engagement with the potential of robotics. His concepts have been adapted into various cinematic works since, including the 1999 Robot film which loosely followed his original narratives while highlighting the complexity of AI and robotics interactions.

Mid-century depictions of robots and robot culture
By the late 20th and early 21st centuries, advancements in AI technology propelled robotics into many fields by introducing innovative solutions to complex problems. The combination of machine learning, computer vision, and real-time data processing allowed robots to perform increasingly complex tasks. Intelligent robots began to automate tasks in manufacturing, healthcare, and aerospace that required precision and endurance beyond human capabilities.

Rosie the Robot appearing in the 60s TV series The Jetsons
The ongoing evolution of robotics and AI continues to be marked by significant breakthroughs, including the development of autonomous vehicles and advanced robotics systems capable of adapting to their environments. As the technology advances, the collaboration between AI and robotics is expected to play an important role in addressing challenges and unlocking new opportunities in society.
 Components of AI Robotics
Components of AI Robotics
AI robotics combines AI with robotics to create intelligent machines capable of autonomously performing tasks. This integration of AI and robotics involves several key components that enhance the capabilities of robots well beyond traditional automation.
Machine Learning
Machine learning is a component of AI that enables robots to learn from data and improve their performance over time without explicit programming. Machine learning algorithms allow robots to adapt to new situations and make decisions based on past experiences. This enhances their operational efficiency and effectiveness in various tasks, ranging from industrial processes to delicate healthcare applications. There are three primary types of machine learning used in AI robotics:
- ⚡ Supervised Learning: In this approach, models are trained on labeled datasets, allowing robots to learn from examples. For instance, a robot can be trained to recognize objects by being shown images of those objects along with their labels.
- ⚡ Unsupervised Learning: This method involves training models on data without labels, enabling robots to identify patterns or groupings independently. An example includes segmenting customers based on their purchasing behavior.
- ⚡ Reinforcement Learning: In reinforcement learning, robots learn to make decisions through trial and error, receiving feedback from their environment. This approach is particularly useful for tasks requiring continuous improvement and adaptation.
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing is a crucial component that allows robots to interact with humans in a meaningful way. Natural language processing enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language, facilitating effective communication and enhancing user experiences. Applications of natural language processing in AI robotics include chatbots, virtual assistants, and automated customer support systems.
Computer Vision
Computer vision is another integral component of AI robotics, enabling robots to interpret and understand visual information from the world around them. Through computer vision, robots can identify and track objects, recognize faces, and navigate complex environments. This capability is essential for tasks such as autonomous driving, surveillance, and robotic surgery.
Sensor Technologies
AI robotics heavily relies on advanced sensor technologies that provide real-time data about the robot's environment. Sensors such as cameras, LIDAR, ultrasonic sensors, and infrared sensors allow robots to perceive their surroundings, making them more situationally aware and capable of responding to dynamic changes in their environment. This enhances their ability to perform tasks autonomously and safely.
Autonomous Decision-Making
The integration of AI allows robots to make autonomous decisions based on the information gathered from their sensors and the learned experiences from machine learning. This ability to evaluate situations and choose appropriate actions enables robots to operate effectively in various scenarios, from industrial automation to personal assistance. By combining these components, AI robotics can achieve remarkable advancements, leading to innovations that significantly impact various industries, including health- care, manufacturing, and space exploration.
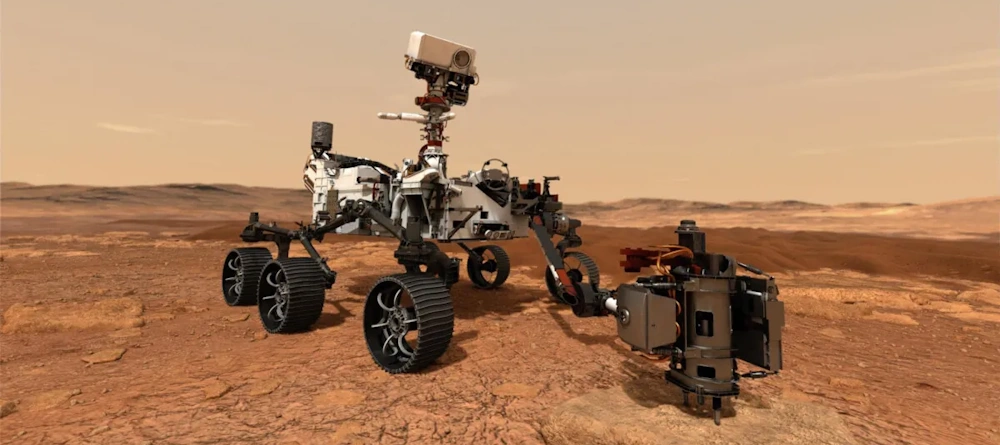

We could say it's the most famous robot in the world, but it's actually on another world; the planet Mars. NASA has sent five robotic vehicles, called rovers, to Mars. The names of the five rovers are Sojourner, Spirit, Opportunity, Curiosity, and Perseverance. Curiosity is the largest robot to ever land on another planet, about the size of a small SUV. It has bigger wheels than the previous rovers, which helps it to roll over rocks and sand without getting stuck.
 Applications
Applications
Healthcare
AI and robotics are making significant strides in healthcare by enhancing patient inter- action and treatment options. Virtual health assistants, such as Sense.ly and AiCure, streamline healthcare delivery by managing tasks like answering patient inquiries, scheduling appointments, and protecting sensitive medical data, thus improving patient engagement and experience. AI-driven applications are being utilized for triaging patients based on symptoms, making healthcare more accessible and efficient. The NHS has successfully implemented such AI chatbots, with around 1.2 million users opting for this service over traditional call methods. Additionally, AI platforms like Tempus and ClosedLoop.ai personalize treatment plans by analyzing vast amounts of clinical and molecular data, ultimately aiding in the management of various diseases.
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, robots are increasingly employed to improve efficiency and productivity by automating repetitive and hazardous tasks. Collaborative robots (cobots) are designed to work alongside human workers, effectively addressing labor shortages while ensuring precision in manufacturing processes. Innovations in robotic grippers allow for the handling of fragile items without damage, facilitating more adaptable production lines. Furthermore, digital twins are becoming common in manufacturing, allowing companies to simulate and optimize operations in real time, significantly enhancing performance and resource allocation.
Transportation
In transportation, AI applications are optimizing logistics and improving the delivery of goods. Drones and robotic vehicles are being tested for last-mile deliveries, while remote robot-assisted surgeries are becoming more prevalent. These advance- ments not only streamline service delivery but also enhance safety and precision in operations, making transportation more efficient overall.
Food Production
Robotics are also transforming food production, which is projected to increase by 50% by 2050. Robots are being deployed for tasks such as milking and planting, helping to reduce costs and enhance efficiency. They also assist farmers in gathering critical data on crop conditions through advanced algorithms and sensor technolo- gies. By automating labor-intensive tasks, robots are vital in adapting to the challenges posed by climate change and ensuring sustainable agricultural practices.
![]()
 AI Robotics Challenges
AI Robotics Challenges
The integration of AI and robotics faces several challenges going forward
A majority of stakeholders have identified technical challenges as major barriers to AI robotics adoption. These challenges often stem from outdated IT infrastructure and a lack of sufficient resources within because of extensive upgrades required to support advanced AI tools. Such upgrades are viewed as resource-intensive, both in terms of financial costs and logistics. For instance, one participant in a recent study remarked on the hesitance to implement AI due to concerns over the need for a complete overhaul of their current IT systems:
Implementation Costs
The high costs of AI development and implementation are another critical challenge to AI robotics. Estimates indicate that costs for implementing AI can range from $6,000 to $300,000, influenced by factors such as initial investments and ongoing operational expenses . These costs can pose significant barriers, particularly for smaller organizations or those with limited budgets.
Scalability Issues
The scalability of AI solutions and their interoperability across different platforms remain pressing technical concerns. Organizations must ensure that their AI algorithms can effectively handle complex tasks while being compatible with various systems. This often requires a robust strategy for implementing AI within the existing work culture, enabling organizations to adapt as challenges arise.
 Future Directions
Future Directions
The future of AI and robotics is marked by incredible advancements and the potential for widespread integration into everyday life. As these technologies evolve, we can anticipate transformative applications like Optimus. The development of self-driving cars and smart home devices shows how AI and robotics can revolutionize daily activities and improve quality of life.
Collaboration
In the future, a collaborative relationship between humans and intelligent machines will be commonplace. Continued research and development in AI and robotics promise to unlock new capabilities, enabling robots to perform complex tasks while working alongside human operators. This synergy can enhance productivity and create safer work environments. Engaging stakeholders in discussions about the integration of AI and robotics is important for creating a future that benefits society as a whole.
Public Acceptance
The public's perception of robots will play a significant role in determining the extent of their integration into society. The willingness of individuals to embrace robots in domestic and professional settings hinges on their comfort level with the technology. Addressing safety concerns and encouraging positive narratives about robotic applications will be important for broader acceptance.
Ethics
As the capabilities of AI and robotics grow, so too do the ethical concerns associated with their use. Issues such as job displacement, data privacy, and autonomous decision-making must be carefully evaluaged. The automation of tasks, while enhancing efficiency, raises fears of unemployment and economic inequality, necessitating thoughtful policies that support worker retraining and alternative employment opportunities.
 Upright Posture
Upright Posture
The day the robot family forgot how to walk (and other funny fails)
We take upright posture for granted unless we're two, over 75 or a robot. Meet the clumsy AI robot family doing everyday things wrong in the goofiest ways possible.
Once there was a happy little robot family who lived in a shiny house made of tin foil and old computer screens. There was Mama Bot (who always carried a big spoon), Papa Bot (who loved to dance), Baby Bot (the smallest and bounciest), and DogBot (who barked in binary: “Woof 101010!”).
One sunny morning Mama Bot said: “Time to go to the park, everyone! Let’s walk there!”
But the moment they stepped outside… disaster!
Mama Bot lifted her left foot… and kept it up. She just stood there like a flamingo on a video call. “Um, my leg forgot how to come down,” she said. Then she wobbled and fell backward—BOING!—right into a giant pile of bubble wrap. POP-POP-POP-POP-POP! She giggled so hard her antenna wiggled like a happy worm.
Papa Bot tried to help her up. He took one big step… tripped over his own charger cable… and did the slowest, clumsiest somersault ever. He landed on his head with his legs sticking straight up like two gray straws. “Ta-da!” he shouted from upside-down. “I invented robot yoga!”
Baby Bot thought this looked like fun. She zoomed forward shouting “My turn! My turn!” But she forgot to stop running. She ran straight into a flower bed, face-planted into soft dirt, and came up wearing a big tulip hat. “Pretty!” she said, shaking her head so hard petals flew everywhere like colorful snow.
DogBot wanted to join the silliness. He tried to jump over Papa Bot’s legs, but his springy legs were too springy. He went BOING! way too high, spun in the air like a furry helicopter, and landed in the bird bath with a giant SPLASH! Now he was a soggy robo-pup, dripping water and making tiny bubbles every time he barked: “Woof… glub… 101010… glub…”
By now all four robots were laughing so hard their batteries almost ran out. Mama Bot finally managed to roll over and stand up (still covered in bubble wrap). Papa Bot did a wobbly victory dance on one leg. Baby Bot shook more petals off her tulip hat. DogBot shook himself like a wet towel and sprayed everyone.
And they all decided: “Maybe today we don’t walk to the park. Maybe today we just stay home and fall over again on purpose!”
So they did. They practiced silly falls all afternoon:
Backward flops into pillows
Slow-motion superhero landings
Pretend ice-skating on the kitchen floor (with lots of sliding and crashing)
And every time someone fell down, they shouted: “Ten points for style!” Even when DogBot fell into the laundry basket and came out wearing Mama Bot’s favorite apron like a superhero cape.
And if you ever see a robot lying on the ground with its legs in the air, don't worry, it's probably just practicing for the Robot Floor Exercise at the Olympics.
The End.
 Links
Links
AI is Just an App is a collection of hilarious short stories that shine a light on our digital future.
More AI Stories.
Optimus robot by Tesla.
Robots in Industry page.
External links open in a new tab:
- Robot Design and Architecture: Key Principles and Practices
- Three Laws of Robotics - Wikipedia
- AI in Robotics: 6 Groundbreaking Applications - v7labs.com
- Top 10 Robotics Trends & Innovations in 2025 | StartUs Insights
- Achievements of robotics in 2023 and What new technologies can we expect
- The Future of Robotics and Artificial Intelligence:
- Robotics | Stanford Emerging Technology Review
- Artificial Intelligence Vs Robotics
- Smart Sensing and Adaptive Reasoning for Enabling Industrial Robots
- AI vs Robotics
- Artificial Intelligence in Robotics: Practices and Applications
- The Challenges, Possibilities and Ethics of AI-Enabled Robots